Key Pros and Cons of Blockchain in Healthcare
Key Pros and Cons of Blockchain in Healthcare
"Blockchain" is one of the most prominent of the ever-growing list of tech buzzwords that resonate in articles across the web. In fact, there is much excitement surrounding the potential of Blockchain technology in the healthcare sector, but few practical applications of how the technology has been implemented in real-world healthcare settings.
This year promises to be a great one for Blockchain, with companies and startups clamoring to harness the potential of Blockchain. This includes ongoing attempts by larger corporations around the world to incorporate blockchain into their systems, including banks, healthcare organizations, manufacturing companies, etc., and some of them have enjoyed some success that is expected to increase even further.
But what are the real key pros and cons of Blockchain?
Let’s begin with a bit of context. Blockchain was originally developed for cryptocurrencies in order to eliminate the need for intermediaries, such as banks, while at the same time protecting against a high risk of fraud and theft.
In the healthcare sector, transparent and immutable record-keeping transactions can also be important, such as purchase and shipping transactions in the supply chains of medical equipment and pharmaceuticals; as well as the tracking of permits and staff access to facilities, medical records, or other health data.
Pros of Blockchain in Healthcare
#1. Blockchain is a major change from traditional approaches to data management.
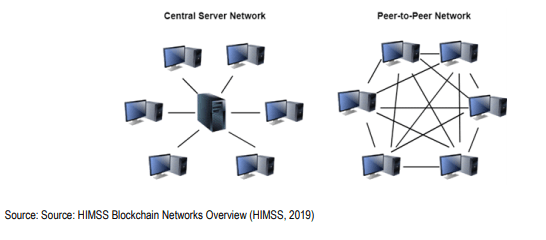
In a traditional database, the data is kept on a single central server (or network of servers) with a centralized database manager. Instead, Blockchain is an approach to managing data where there is an electronic ledger attached that is distributed across a peer-to-peer network without central management of the data.
A centralized network vs. distributed peer-to-peer network
#2. Blockchain adapts to situations where the transparency and immutability of data is needed
Blockchain is best suited to recording transactions with a lightweight fingerprint, where transparency and immutability are an advantage. In other words, it is better suited to situations where there is less trust between the participants of a network and the size of the data blocks is relatively small. Situations in healthcare where Blockchain can be particularly useful include verifying the identity of patients, vendors, or vendors; supply chain management; and management of the dynamic consent of the patient for the use of data.
#3. Management of patient consent and data access permissions
Blockchain can be a transparent and auditable way for people, using their unique credentials and encryption key, to allow other parties to access your personal health data. This includes granting authority to healthcare professionals, service providers, and other relevant actors (for example, researchers and social care providers) to access your medical records and other information for the purpose of providing direct healthcare or to enable research, statistics or other secondary uses of your data.
Since electronic data can be used and reused ad infinitum, and new research questions and purposes for data use continually arise, Blockchain-enabled incremental or 'dynamic' consent provides a very useful alternative to 'general or one-time ' consent models. If a person decides to change their permission or consent terms, the changes can be added as a new block that overrides the previous instructions in the chain.
Cons of Blockchain in Healthcare
#1. Blockchain development cost
Although the cost of establishing, maintaining and upgrading a healthcare Blockchain is unknown, there are several US web development companies or US custom software development company that charge on their own. However, it is not yet known what the market standard really is.
Cost is a dominant factor affecting the overall decision to implement Blockchain technology in the healthcare industry.
Aside from the cost, there are 4 major data challenges in the healthcare industry
#2- Blockchain can't go backwards: data is immutable
Data immutability has always been one of Blockchain's biggest downsides. It is clear that multiple systems benefit from it, including the supply chain, financial systems, etc. However, if you look at how networks work, you need to understand that this immutability can only be present if the nodes in the network are all fairly distributed.
What I mean is that a Blockchain network can be controlled by an entity if it owns 50% or more of the nodes, which makes it vulnerable.
Another problem is that once written, the data cannot be deleted. Every person on Earth has the right to privacy. However, if the same person uses a digital platform that runs on Blockchain technology, he will not be able to remove his trace from the system if he does not want it there. In simple words, there is no way that you can remove the trace of it, leaving the privacy rights in pieces.
#3- Expert knowledge
Implementing and managing a Blockchain project is difficult and it therefore requires a deep knowledge of the company in order to go through the entire process.
There is a need to hire multiple experts in the field of Blockchain, which is a problem and thus counts as one of the disadvantages of blockchain.
Not only that, they also need to train existing professionals on how to use Blockchain and make sure that the management team can understand the complexities and results of a Blockchain-powered business.
This way they can understand your requirements and help transform your business processes to use Blockchain.
In addition, Blockchain developers and specialists are harder to find and will thus cost more compared to traditional developers due to their supply and demand ratio.
Final thoughts …
Although these are just a few of the pros and cons of Blockchain, it should be noted that this technology has disruptively changed the way that many industries, including healthcare, handle information security.
Also, there are newer Blockchain solutions that offer better solutions compared to the first generation of Blockchain technology. For example, Ethereum solved the inefficiencies by switching to a better Blockchain technology solution where there is a form of automation that use smart contracts and has also adopted Proof of Stake (PoS), which is notably more efficient than Proof of Work (PoW).